We Are Open 24 Hours a Day, 7 Days a Week, Including Weekends and Public Holidays.
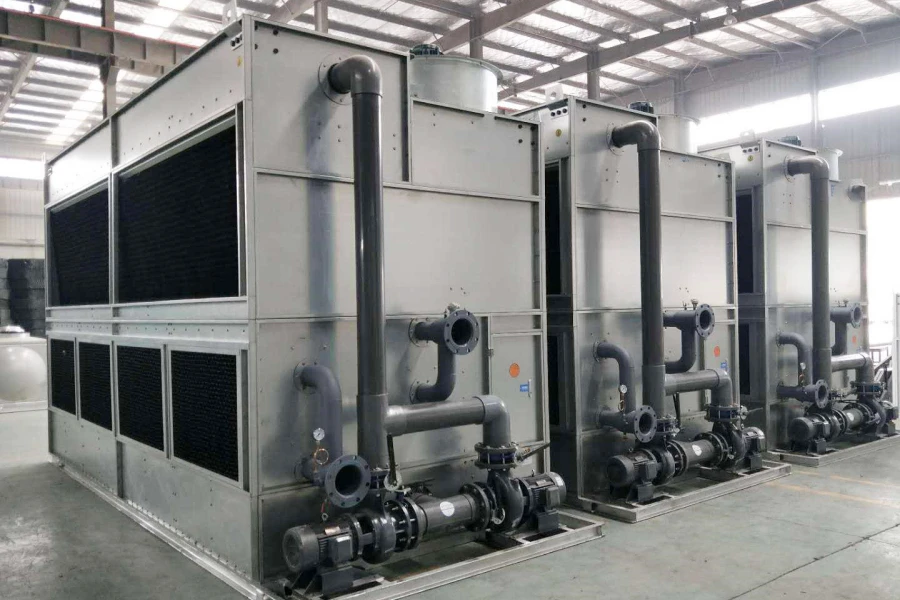
Circular Cooling Tower: Comprehensive Introduction
- 1.Overview
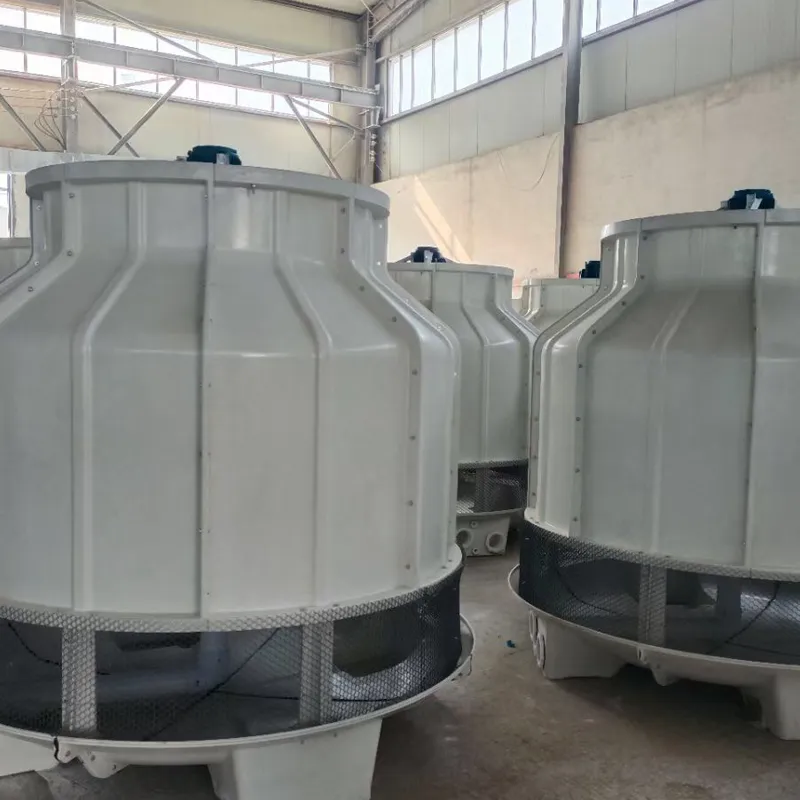
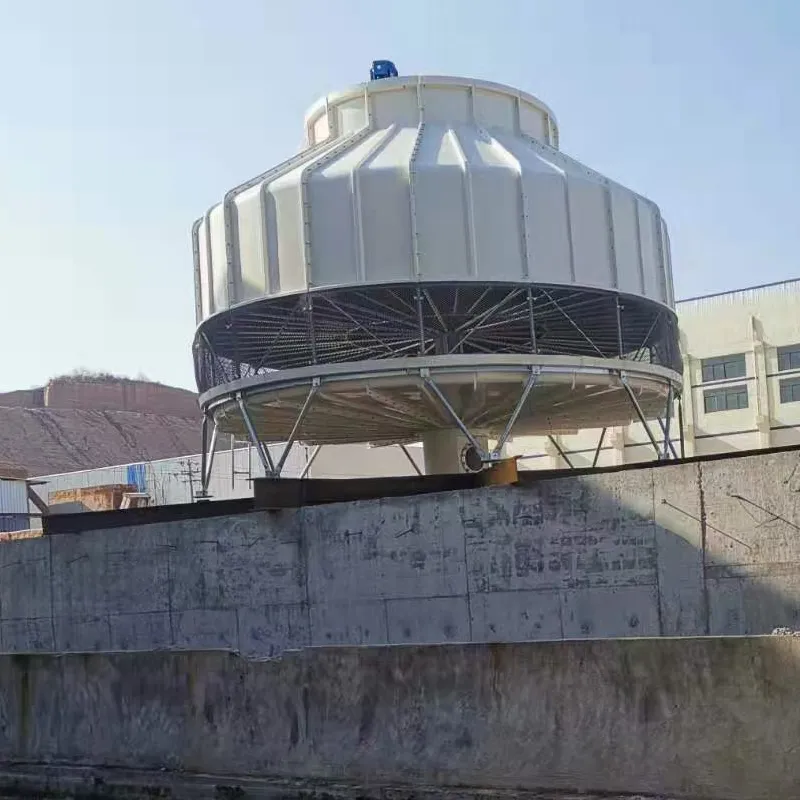
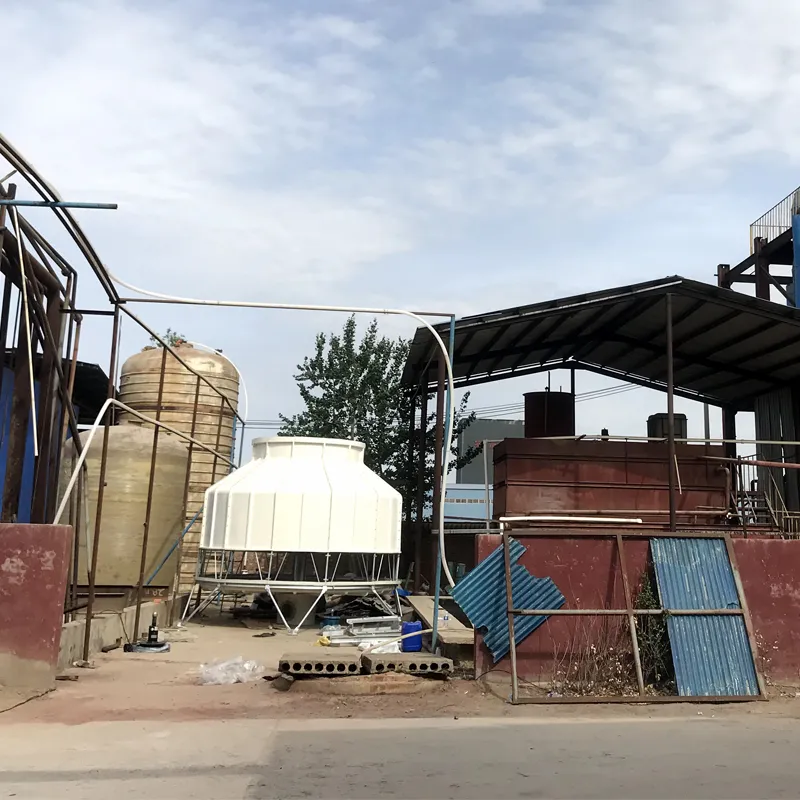
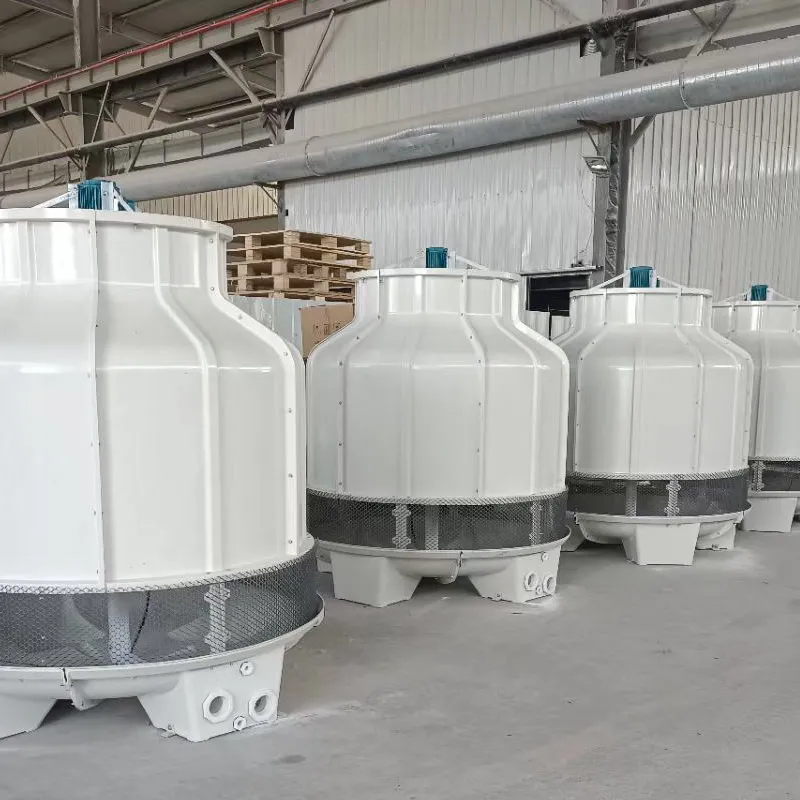
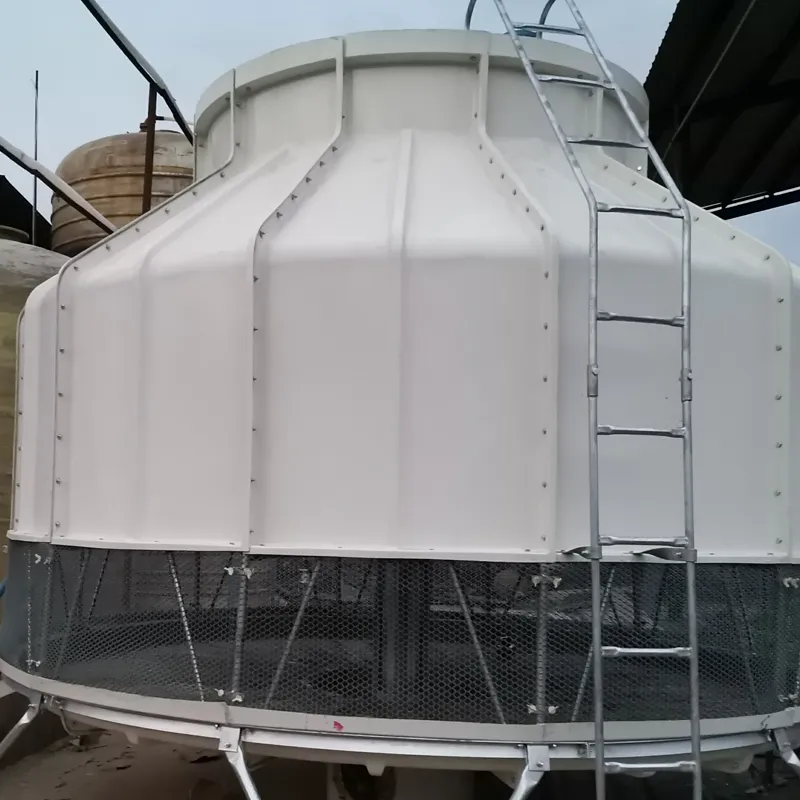
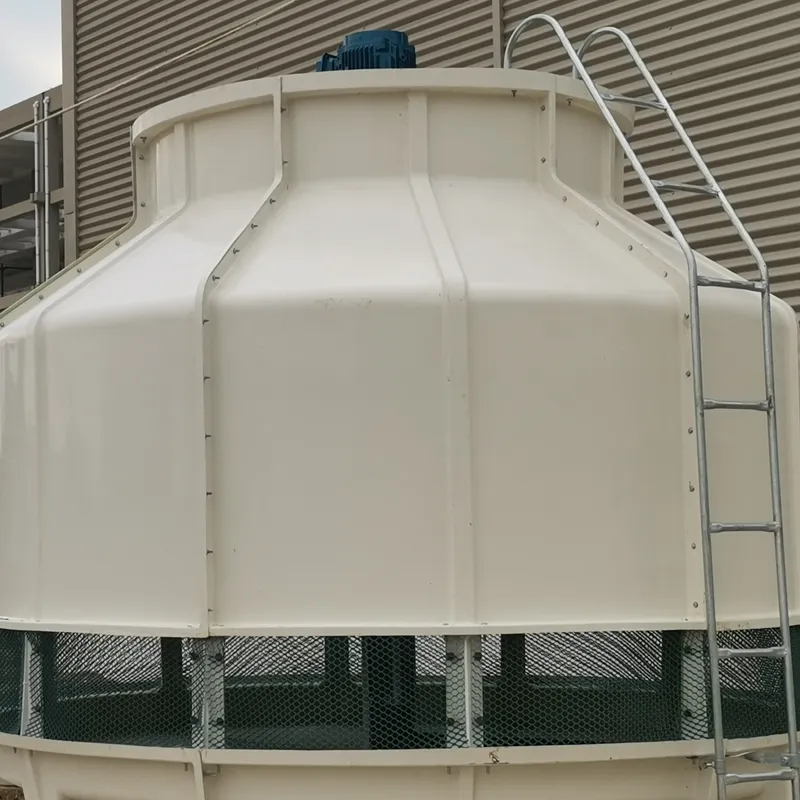
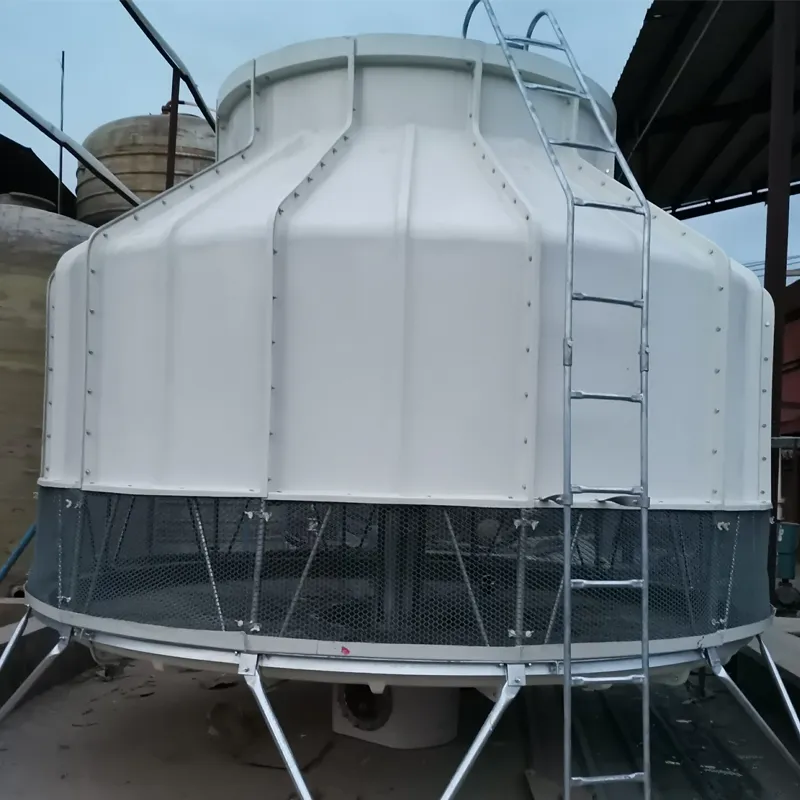
circular cooling tower is a type of mechanical draft cooling tower designed with a cylindrical structure to optimize heat exchange efficiency. It is widely used in industries such as power generation, petrochemicals, and HVAC systems to dissipate waste heat by evaporating water. Its circular shape enhances airflow dynamics, structural stability, and ease of maintenance.
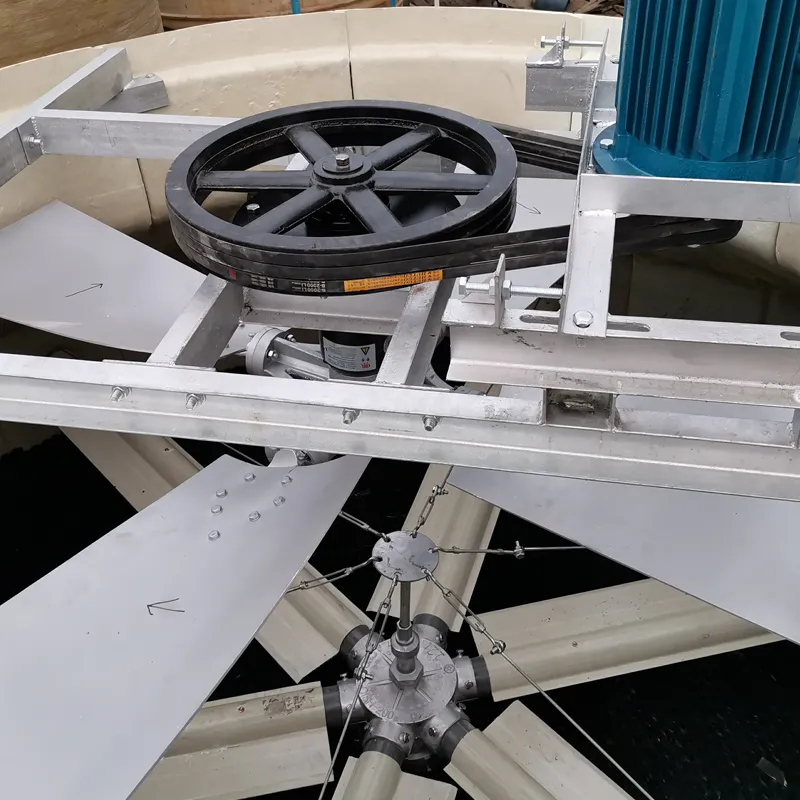
- 2.Key Components & Design Features
Structure:
Material: Typically constructed from fiberglass-reinforced plastic (FRP) for corrosion resistance, durability, and lightweight properties.
Shape: Cylindrical design reduces wind load stress and improves structural integrity.
Heat Exchange System:
Fill Media: High-efficiency PVC or PP fills maximize air-water contact for effective cooling.
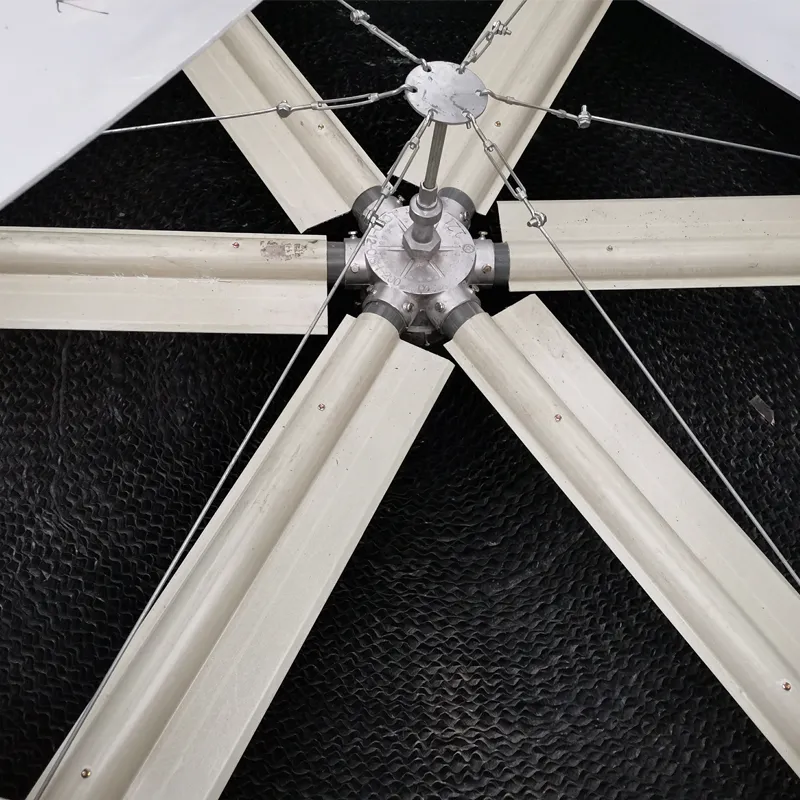
Water Distribution: Radial arms with nozzles ensure even water dispersion over the fill material.
Airflow Mechanism:
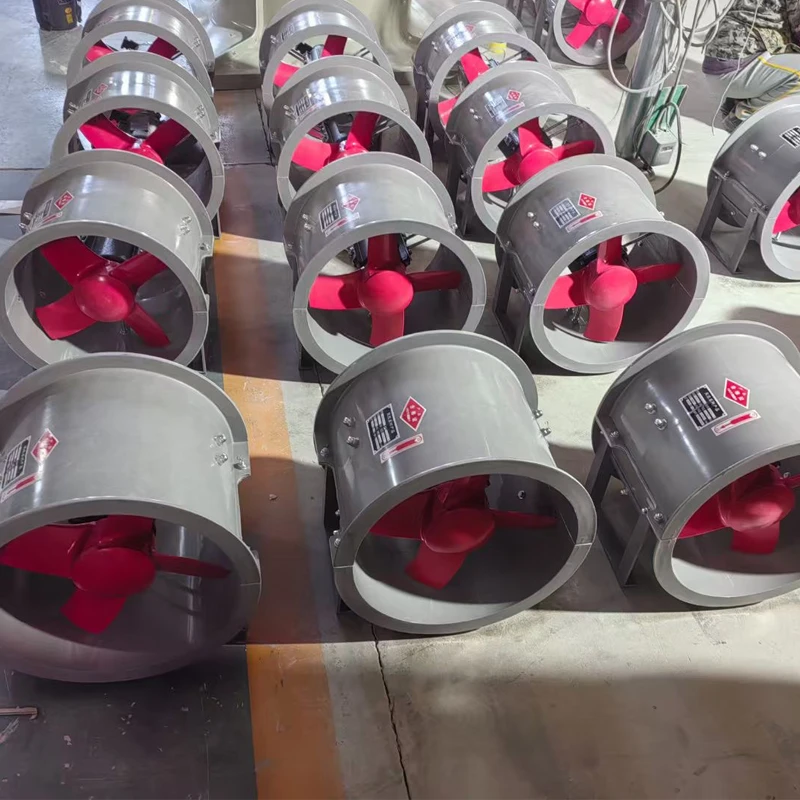
Induced Draft Fan: Centrally located at the top to pull air upward (counterflow design) through the tower.
Drift Eliminators: Radial arrangements minimize water droplet escape, reducing environmental impact.
- 3.Working Principle
- Hot Water Inlet: Warm water from industrial processes is pumped to the distribution system.
- Water Distribution: Nozzles spray water evenly over the fill media.
- Airflow: Fans draw ambient air upward, creating a counterflow with the falling water.
- Heat Transfer: Evaporation cools the water, which collects in the cold water basin for recirculation.
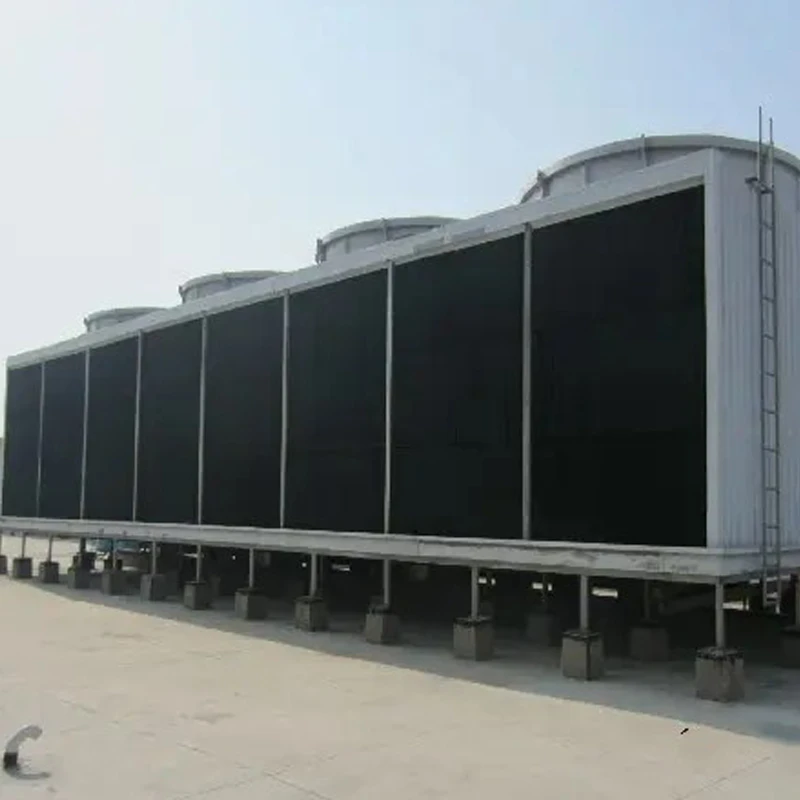
- 4.Types of Circular Cooling Towers
Counterflow Design: Air moves upward against the downward flow of water (most common).
Crossflow Design: Air moves horizontally across the water stream (less common in circular towers).
Hybrid Systems: Combine dry and wet cooling for water conservation.
- 5.Advantages
Efficiency: Uniform airflow reduces energy consumption by 15–20% compared to rectangular towers.
Durability: FRP construction resists corrosion, UV radiation, and chemical exposure.
Low Maintenance: 360° accessibility simplifies inspection and component replacement.
Space Utilization: Compact footprint suits installations with radial space availability.
- 6.Applications
Power Plants: Cooling condenser water in thermal and nuclear plants.
Oil & Gas: Heat management in refineries and petrochemical complexes.
HVAC Systems: Large-scale commercial building climate control.
Manufacturing: Temperature regulation in steel, plastics, and food processing.
- 7.Challenges
Initial Cost: Higher upfront investment than rectangular towers (offset by long-term efficiency).
Space Constraints: May require strategic placement due to circular footprint.
Retrofitting: Compatibility issues with existing rectangular infrastructure.
- 8.Environmental Considerations
Water Conservation: Advanced drift eliminators reduce water loss to <0.001% of circulation flow.
Energy Savings: Optimized airflow lowers fan power demand, cutting CO₂ emissions.
- 9.Comparison with Rectangular Cooling Towers
Feature Circular Cooling TowerRectangular Cooling Tower Airflow EfficiencyUniform distribution, less turbulence Potential for uneven airflow Footprint Radial space optimized Linear layout suits narrow spaces Maintenance Full perimeter access Limited by corners and partitions Wind Resistance | Superior structural resilience Prone to wind-induced stress
- 10.Conclusion
Circular cooling towers excel in efficiency, durability, and operational stability, making them ideal for industries prioritizing long-term performance and energy savings. While initial costs and spatial requirements may pose challenges, their environmental benefits and low lifecycle costs position them as a sustainable choice for large-scale heat dissipation needs.
What Our Customers Say About Circular Cooling Tower
Circular Cooling Tower FAQ
-
Q: What is a circular cooling tower?
A: A circular cooling tower is a type of cooling system with a round shape, designed to efficiently reject heat from industrial processes.
-
Q: What industries benefit from circular cooling towers?
A: Circular cooling towers are commonly used in power generation, chemical plants, and manufacturing industries.
-
Q: What are the key advantages of a circular cooling tower?
A: Circular cooling towers offer space efficiency, high cooling capacity, and easy maintenance.
-
Q: How do circular cooling towers compare to other types?
A: Circular cooling towers are more compact and can handle higher heat loads with minimal space, making them suitable for smaller industrial facilities.







Address
20 Xingyuan South Street, Zaoqiang County, Hengshui City, Hebei Province, China